Australia’s Environmental Struggles: Climate Change, Bushfires, and Conservation Solutions
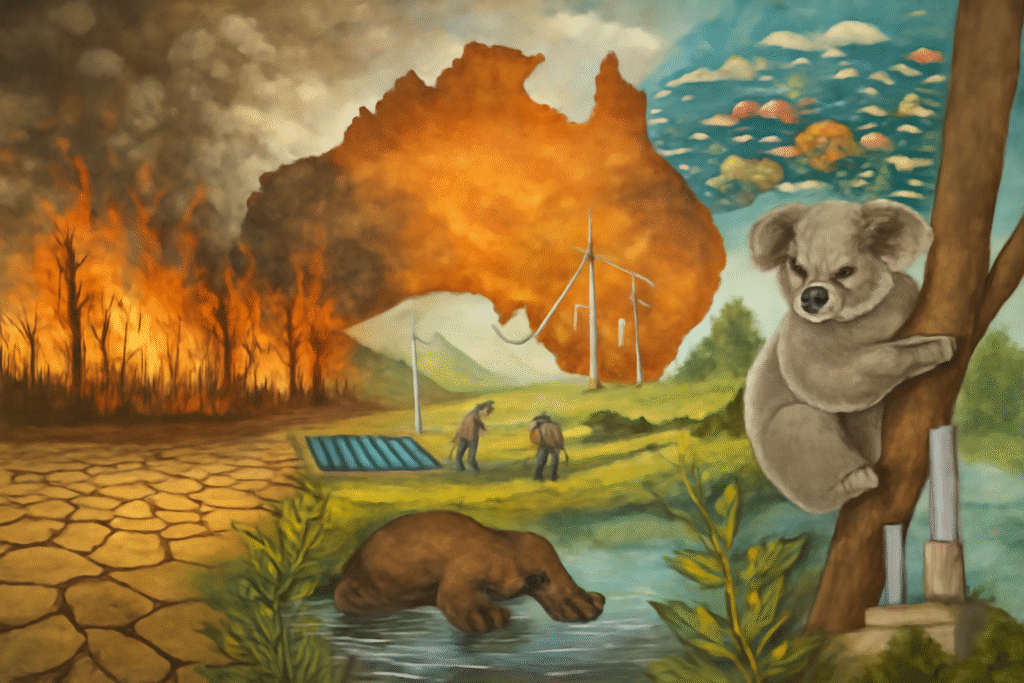
Australia is facing a complex set of environmental challenges, many of which are directly linked to the global crisis of climate change. The country’s vast and varied landscapes, from dense rainforests to arid deserts, are increasingly affected by the changing climate. Rising temperatures, shifting weather patterns, and extreme events like floods, droughts, and bushfires are having widespread impacts on Australia’s ecosystems, wildlife, and communities.
One of the most noticeable effects of climate change in Australia is the increase in bushfire intensity. These fires, although a natural part of the Australian landscape, have become more frequent and devastating due to rising temperatures and prolonged drought conditions. The 2019-2020 bushfire season, known as “Black Summer,” burned millions of hectares and caused irreparable harm to both the environment and human communities. The fires destroyed forests, habitats, and killed millions of animals, some of which may be facing extinction. The severity of these fires underlines the urgent need for comprehensive climate action.
Droughts have also become a recurring issue for Australia, with many regions experiencing water shortages and reduced rainfall. The country’s agricultural industry, which plays a major role in its economy, is particularly vulnerable to drought conditions. Water scarcity affects both crop production and livestock farming, leading to economic instability in rural areas. Additionally, increasing salinity in the soil threatens the long-term viability of farming practices in these regions.
Another crucial aspect of Australia’s environmental crisis is the decline of its iconic Great Barrier Reef. Coral bleaching, caused by elevated sea temperatures, has severely damaged the reef, threatening the rich marine biodiversity it supports. The loss of coral reefs not only impacts marine life but also has economic repercussions for industries like tourism and fishing, both of which rely heavily on the health of the reef.
In response to these environmental challenges, Australia is working on various conservation initiatives aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change. The country has committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions under international agreements like the Paris Agreement. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power is central to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate impacts.
Efforts to protect and restore Australia’s ecosystems are equally vital. National parks and nature reserves are being expanded to preserve the country’s unique flora and fauna. In particular, efforts are being made to protect endangered species like the koala, which has been severely impacted by the destruction of its habitat in bushfires.
Another growing trend in Australia’s conservation efforts is the inclusion of Indigenous land management practices. Traditional fire management techniques, such as controlled burns, are being adapted to modern fire control strategies to prevent the spread of wildfires and promote ecosystem health. This fusion of traditional knowledge and modern science is helping to create more resilient landscapes.
Ultimately, Australia faces significant challenges in combating climate change and protecting its environment. However, with strong political will, community engagement, and innovative conservation strategies, there is hope for mitigating the worst effects of climate change and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.







